Alphabets Page #8
This page lists all the various symbols in the Alphabets category.

An alphabet is a standard set of letters (basic written symbols or graphemes) that is used to write one or more languages based on the general principle that the letters represent phonemes (basic significant sounds) of the spoken language. This is in contrast to other types of writing systems, such as syllabaries (in which each character represents a syllable) and logographies (in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic unit).
Symbols in this category:
Gāmal
Gimel is the third letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Gīml Phoenician gimel.svg, Hebrew ˈGimel ג, Aramaic Gāmal Gimel.svg, Syriac Gāmal ܓ, and Arabic ǧīm ج (in alphabetical order; fifth in spelling order). Its sound value in the original Phoenician and in all derived alphabets, save Arabic, is a voiced velar plosive [ɡ]; in Modern Standard Arabic, it represents either a /d͡ʒ/ or /ʒ/ for most Arabic speakers except in Lower Egypt, the southern parts of Yemen and some parts of Oman where it is pronounced as a voiced velar plosive [ɡ], see below and also Persian Gaf گ.Gimel is the third letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Gīml Phoenician gimel.svg, Hebrew ˈGimel ג, Aramaic Gāmal Gimel.svg, Syriac Gāmal ܓ, and Arabic ǧīm ج (in alphabetical order; fifth in spelling order). Its sound value in the original Phoenician and in all derived alphabets, save Arabic, is a voiced velar plosive [ɡ]; in Modern Standard Arabic, it represents either a /d͡ʒ/ or /ʒ/ for most A
Gimel (South Arabian alphabet)
The letter "g" as rendered in the South Arabian alphabet.
Gimel Letter
Gimel is the third letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Gīml , Hebrew ˈGimel ג, Aramaic Gāmal , Syriac Gāmal ܓ, and Arabic ǧīm ج (in alphabetical order; fifth in spelling order).
gīml
Gimel is the third letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Gīml Phoenician gimel.svg, Hebrew ˈGimel ג, Aramaic Gāmal Gimel.svg, Syriac Gāmal ܓ, and Arabic ǧīm ج (in alphabetical order; fifth in spelling order). Its sound value in the original Phoenician and in all derived alphabets, save Arabic, is a voiced velar plosive [ɡ]; in Modern Standard Arabic, it represents either a /d͡ʒ/ or /ʒ/ for most Arabic speakers except in Lower Egypt, the southern parts of Yemen and some parts of Oman where it is pronounced as a voiced velar plosive [ɡ], see below and also Persian Gaf گ.
Hē
He is the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Hē Phoenician he.svg, Hebrew Hē ה, Aramaic Hē He0.svg, Syriac Hē ܗ, and Arabic Hāʾ ﻫ. Its sound value is a voiced glottal fricative ([ɦ]).
hē
He is the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Hē Phoenician he.svg, Hebrew Hē ה, Aramaic Hē He0.svg, Syriac Hē ܗ, and Arabic Hāʾ ﻫ. Its sound value is a voiced glottal fricative ([ɦ]).
Citation
Use the citation below to add this symbols category to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Alphabets Symbols." Symbols.com. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 27 Jul 2024. <https://www.symbols.com/category/66/Alphabets>.






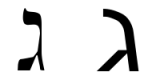


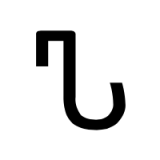



Have a discussion about the Alphabets category with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In